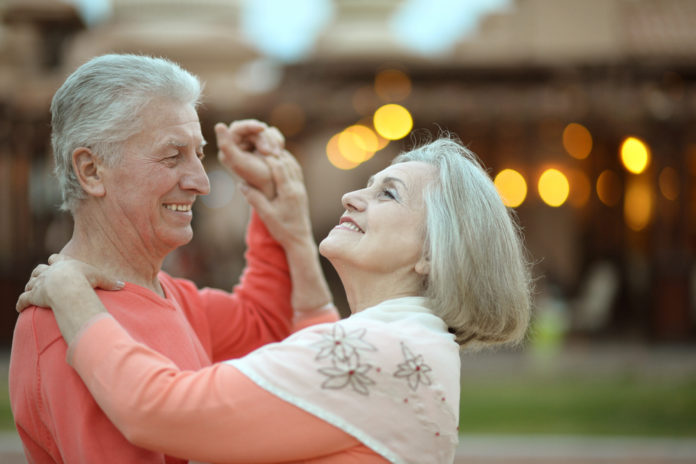
According to a literature review involving over 18 articles five different styles of dance, including ballroom, contemporary, cultural, pop, and jazz, research found dancing can significantly improve muscular strength and endurance, balance, and other aspects of functional fitness in older adults.
They further concluded, “Future researchers may want to analyze the effects of dance on mental health.”
Oh and researchers have…
The Mental Health Benefits of Dance
Queensland Ballet undertook research regarding the health and wellbeing benefits of ballet amongst mature adults. The three-month project incorporated 10 Ballet for Seniors classes, which were observed by a researcher for data collection.
Ultimately, the summary findings of the report concluded participants experienced higher energy levels, greater flexibility, improved posture, and an enhanced sense of achievement.
But while such physical benefits of movement and dance on ageing bodies are already well-documented, the findings further highlighted the joy and benefits social connections dance can bring to people’s lives, as participants also expressed greater feelings of happiness and enjoyed a sense of community and friendship.
Dance has also shown to improve cognitive performance and reaction times, touting the practice as an effective treatment option for a number of conditions, including depression and Parkinson’s disease.
Furthermore, research published in the New England Journal of Medicine found among leisure activities, reading, playing board games, playing musical instruments, and dancing were associated with a reduced risk of dementia.
When comparing dance with endurance training, evidence shows each has an anti-aging effect on the brain. However, only dancing corresponded to a noticeable difference in behavior, which researchers attribute to the extra challenge of learning dancing routines.
How Does Dance Affect the Brain?
Dance affects the brain as soon as the music starts.
Music on its own stimulates the brain’s reward center and releases dopamine, also known as that “feel good” hormone, and reduces the stress hormone cortisol, with the combination successively causing greater feelings of happiness, excitement, and joy.
Pairing physical movements with the music further activates numerable portions of the brain, including the motor cortex, somatosensory cortex, basal ganglia, hippocampus, and cerebellum, with the totality involved in motor control, voluntary movement, coordination, memory, and learning.
Nonetheless, these stimulations and adaptations that transpire when dancing has seamlessly improved the mental and physical health of seniors.
Ready to dance your way to a healthier brain?
Simply turn on some music on move to the beat at home or find dance classes near you, including at community recreational centers, senior centers, and local dance studios!
But in addition to dance and physical movement, an overall healthy lifestyle (including a good diet, adequate sleep, and stress management) also help keep the brain stay young!