Wondering how to stay healthy after 60? Although it’s often easier said than done, a healthy lifestyle does come down to keeping a few key healthy habits.
Luckily, many healthy aging tips are easy to follow and require minimal effort to implement. Keep reading for tips for healthy aging, including ideas for incorporating healthy habits into your daily routine as an older adult.
What Are Health Habits?
As their name suggests, health habits are key practices that contribute to a healthy life. They are habits, routines, and schedules linked to increasing wellness.
Staying hydrated is a prime example—whether you have a schedule, alarm, or some other sort of routine reminder to prompt better drinking habits, avoiding thirst through replenishing fluids is known to have remarkable benefits for human health.
The importance of healthy habits cannot be overstated since even small habits can make a big difference when continued over time. Luckily, health habits don’t have to be multiple steps long to do the trick. Many simple steps can adequately meet your nutrition, exercise, and other needs.
Healthy Habits for Seniors
The following healthy habits can help you live longer without taking up too much extra time in your schedule.
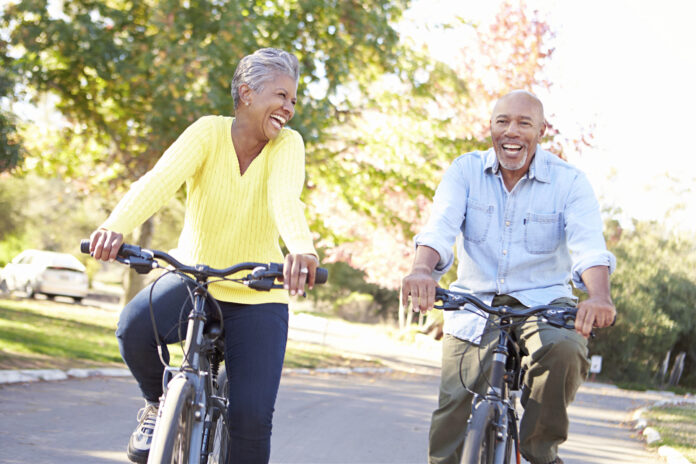
Find Enjoyable Exercise
For adults aged 50 and older, at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity physical activity per week is recommended. This breaks down roughly 20 to 30 minutes of exercise each day.
Even 20 minutes a day can feel like a lot if you aren’t currently exercising. Work your way up to more movement by starting to work out on odd or even days a week.
Alternatively, many seniors find exercising 5 days a week effective—usually on the weekdays while friends and family work. This frees their weekends for grandkids or other obligations such as community functions and church services.
While a mix of cardio and muscle-strengthening exercises are recommended, the type of exercise you do is largely up to personal preference. Instead of forcing yourself to do an activity you loathe, find a method of movement you love! For example, yoga, dancing, or gardening may bring you joy while building your muscles.
Attend Regular Check-Ups & Screenings
Managing health care can sometimes feel tricky, but attending regular doctors’ appointments is crucial to keeping you in good shape. For example, it’s usually recommended that patients over 45 years be screened for colon cancer.
While many cancers can’t be prevented, regular screening is crucial to catching and treating colorectal cancer in the early stages.
Try Healthy Eating Hacks That Resonate With You
Fortunately, you don’t have to try every single healthy eating tip or trick that comes your way. Not every tip you hear (especially online) will be correct, but there are simple quips from experts that may make sense of your lifestyle.
For example, “Make half your grains whole” not only rings true but is catchy and easy to remember! Switching out refined grains for whole grains whenever you can helps to fortify your body against chronic diseases.
Looking for a few other healthy tips that are simple, quick, and easy? Try these healthy hacks that are also easy to remember:
- “Bread, drink, or dessert”- Experts recommend choosing one of these options at each meal, but not all three.
- “Don’t drink your calories”– Steer clear of sugar-sweetened beverages.
- “Eat the rainbow”– Add color to your plate with plenty of fruits and vegetables.
- “Pay the farmer now or the doctor later”– Opt for plant-based picks (like grains, fruits, and vegetables) over ultra-processed foods.
Aim for a Healthy Weight
This may initially sound like vague advice since staying at a healthy weight requires so many other aspects of health to work together synergistically—like diet and exercise. However, being underweight, overweight, and obese are all linked with less-than-optimal health outcomes.
Although it may require some effort in multiple areas of wellness, maintaining a healthy weight can have a big payoff in terms of preventing disease and promoting health. If you don’t know where to start, consult with your healthcare team.
In particular, a dietitian may have guidance regarding certain foods that can assist you in your goals—whether you need energy- and nutrient-dense foods for healthy weight gain or nutrient-rich, low-calorie foods for weight loss. Your doctor can also help you to track trends in your weight over time to see if you’re staying in a “normal” weight window.
Connect with Loved Ones Over Wellness
Studies are still diving into the complexities of social isolation, but what is known is that seniors are particularly susceptible to loneliness and the risks that come along with aging in place alone. It goes beyond preventing falls and fractures— research shows that regardless of age, humans need connection for optimal mental and physical functioning.
Coupling health habits with your social activities can be a great way to accomplish multiple goals simultaneously! For example, walking with friends each morning or attending a cooking class with your spouse can be great ways to connect while also making progress toward your goals.
How to Adopt Healthy Habits
Convinced about the benefits of healthy habits but don’t know where to begin? Try these three habits to help kickstart your new routine.
Habit-Stacking
A trendy term among youth is also making its way to the masses. Habit-stacking, a term used to describe linking or “stacking” habits together, is thought to make health habits more likely to be kept. It’s accomplished by adding a health habit you’d like to have with one you already do.
For example, if you’re interested in meditating, don’t have a ton of free time, but already take a daily walk, you could try a walking meditation. If walking is already a habit, this likely won’t be a big change, and you will be more likely to keep the healthy habit of meditating since it’s attached to a habit you already keep regularly.
Simple Swaps
As mentioned above, sometimes simple tips are the answer to wellness. Instead of completely complicating matters by overturning your current routine, stick with simple switches to get you started.
Simple swaps are effective for most seniors and protect against major health threats, including heart disease). For example, select whole wheat instead of white when shopping for bread. For protein options, lean towards leaner proteins—like fish or poultry—instead of red meat or processed meats. Overhauling your entire diet isn’t necessary since many times small shifts can make a big difference.
Support Progress With Sleep and Stress Management
Many people have no problem maintaining healthy habits during good times but struggle to stay routine when sleep slips, or stress gets out of hand. First off, it’s important to note that this is normal! Adjust to stress, illness, injury, or other troubling situations.
It may sound counterintuitive, but devoting effort and energy to sleep and stress management during these periods of time can serve you well. Although diet and exercise are often considered the main major aspects of wellness, they operate best when the body gets enough sleep.
Additionally, stress can wreak havoc on the body, so it’s crucial to support your health habits with healthy stress management techniques. Essentially, healthy sleep and stress management enhance all your other healthy habits! Without these skills, you may struggle to see the progress you’re searching for in other areas of health.
Healthy Habits for Seniors: The Final Bite
It’s tricky to boil a healthy lifestyle down to just a couple of habits, but science suggests a few key aspects of health are crucial to preventing and managing disease risk. Namely, diet and exercise play a major role, and meeting adequate levels for seniors can do wonders for wellness.
Additionally, attending regular appointments, cultivating connections, getting enough sleep, and finding healthy coping methods can help older adults thrive during their daily routines. Interestingly, science is beginning to support habit-stacking, a novel approach that links new habits to ones you already keep—which may make you more likely to keep them in the long run!