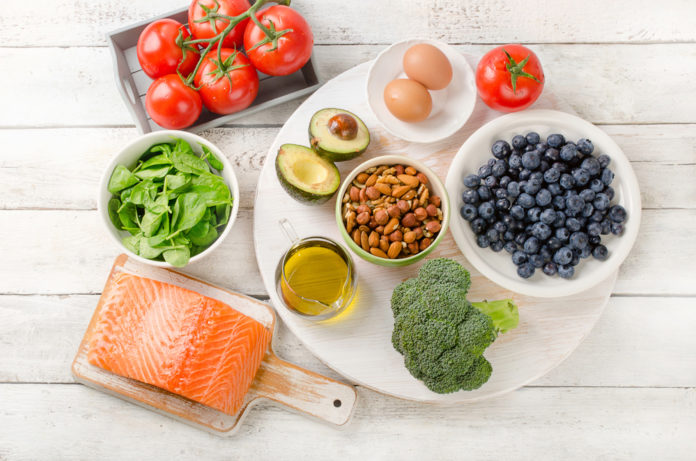
An anti-inflammatory diet aims to minimize harmful inflammation in the body. From avocados to turmeric, fill your diet with this anti-inflammatory food list!
The Top 20 Anti-Inflammation Foods
1. Avocados
Avocados are unique in the fact they are rich in healthy fat, unlike most fruits that naturally supply carbohydrate. They also source a number of antioxidants, including lutein and zeaxanthin that can protect the eyes from cataracts and macular degeneration, common conditions in the elderly. Avocadoes have been shown to reduce inflammation in young skin cells, along with managing blood pressure and promoting digestive health relative to its high fiber and potassium concentrations.
2. Blueberries
They may be small, but blueberries are nothing short of mighty. Blueberries are chock-full of fiber, vitamins, and minerals, along with supplying antioxidants such as anthocyanins, gallic acid, and resveratrol. The compounds can help combat against inflammation, boost immunity, reduce heart disease risk, and improve skin health. Strawberries, blackberries, raspberries, and other colorful berries are also suppliers of powerful antioxidants.
3. Beets
The deep and rich color of beets is not only eye-appealing, but signifies its potent antioxidant content. Beets contain betalain, a pigment supplying their signature color and an excellent anti-inflammatory. Primarily related to its nitrate content, research additionally shows drinking beet juice may fight the progression of dementia. Nitrites have shown to widen blood vessels, thus increasing oxygen-rich blood flow to the brain.
4. Bone Broth
Bone broth is created by simmering together water, animal bones, vegetables, and various seasonings, with the long and slow process releasing valuable minerals from the bones and collagen from the joints. Largely in the form of minerals, antioxidants in bone broth may demonstrate the power to fight against aging by protecting the body from damaging free radicals, harmful compounds mostly originating from environmental toxins or stemming from a poor diet.
5. Broccoli
As if there was just another reason to eat your broccoli… The cruciferous veggie supplies potent antioxidants, including sulforaphane. The antioxidant has shown to fight inflammation by reducing levels of cytokines, signaling proteins shown to synergize inflammation. Research has also shown consuming cruciferous vegetables, including cauliflower and Brussels sprouts, is associated with a decreased risk of both heart disease and cancer.
6. Cherries
Cherries are one of the best foods to reduce inflammation, with researchers suggesting both tart and sweet variations display the highest anti-inflammatory content of any food! They are packed with antioxidants, such as anthocyanins and catechins, which can lower inflammation related to arthritis and muscle recovery.
7. Coffee
Reaching for that morning cup of joe not only gifts that energy jolt, but supplies powerful antioxidants. Along with reducing inflammation, coffee is tied to better brain health and may enhance memory, reduce dementia risk, lower the risk of Parkinson’s disease, and stave off depression. However, it is important to divvy away from copious amounts of added sugars and creams, as they can be pro-inflammatory and dismiss the benefits of coffee.
8. Dark Chocolate
Simultaneously kick the craving and up the antioxidants! Dark chocolate contains polyphenols are powerful antioxidants, showing to lower the risk of cardiovascular disease, certain cancers, and brain deterioration. But to have your chocolate and eat it too, it is important to keep sugar minimized; use cocoa powder in cooking and look for dark chocolate products with minimal added sugars.
9. Fatty Fish
Including salmon, anchovies, herring, mackerel, tuna, and sardines, fatty fish are rich in omega-3 fatty acids. Fatty fish contain high amounts of the omega-3 fatty acids eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), which offers anti-inflammatory effects to the body.
10. Flax and Chia Seeds
Not a fan of fish? Both flax and chia seeds seeds are likewise rich in omega-3 fatty acids, along with being a valuable plant-based protein and fiber source. So in addition to reducing inflammation in the body, these seeds support digestive and heart health.
11. Grapes
Several plant compounds in grapes, including flavonoids and resveratrol, can reduce inflammation and protect against damage, particularly related to cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease.
12. Green Tea
Going green with your tea pours out bountiful health benefits, mostly related to its catechin content, a type of polyphenol. Green tea has demonstrated to reduce inflammation and protect cells from damage that may lead to disease, including diabetes, heart disease, and cancer. Regular consumption may also assist in weight loss efforts by increasing metabolism and reducing fat mass.
13. Leafy Greens
Leafy greens are extremely high in polyphenols and vitamins A, C, and K, all of which are believed to offer anti-inflammatory properties. From spinach to kale, add leafy greens to a number of meals, including salads, soups, casseroles, and soups.
14. Nuts
Almonds, walnuts, and other nut varieties are rich in healthy fat shown to combat against inflammation. In fact, evidence correlate nuts with reduced markers of inflammation, along with a lower risk of cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Nuts are also rich in protein and fiber, two dietary components that facilitate and accelerate weight loss efforts.
15. Oats
Oats are a whole grain that seem to have special health properties, notoriously known for its role in digestive and heart health thanks to its high fiber content. However, oats also contain compounds known as avenanthramides, which have shown to offer anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. So rather than pouring out a sugary bowl of cereal in the morning, prepare these overnight oat recipes for significant health benefits.
16. Olive Oil
Along with supplying heart-healthy monounsaturated fat, olive oil is a known source of oleocanthal, a phenolic compound shown to offer anti-inflammatory benefits. In fact, oleocanthal has exhibited the same anti-inflammatory response in the body as NSAID ibuprofen, designating it as a safe and natural anti-inflammatory agent.
17. Oranges
Oranges are notorious for their vitamin C content, which can act as a potent antioxidant. Vitamin C helps to reduce the damage from ultraviolet (UV) light exposure, a major risk factor for skin cancer. The vitamin has also shown to reduce skin wrinkling and improve overall skin appearance, while it’s collagen-building properties shape and maintain the structure of bone, tendon, skin, cartilage and all other connective tissue.
18. Red Wine
Being produced from grapes, red wine is notorious for its resveratrol content. Resveratrol becomes more concentrated during the fermentation process, while being more potent in red over white wine. Researchers have correlated resveratrol to numerous health advantages, including good heart health, cancer prevention, and anti-aging. To reap the most benefit of red wine, drink in moderation and verify its consumption will not cause adverse side effects related to medication interactions.
19. Tomatoes
Tomatoes are an excellent source of lycopene, a carotenoid found in pink and red plants. The color-producing pigment has also shown to protect against inflammation, cancer, and skin damage caused by ultraviolet (UV) light that shines from the sun.
20. Turmeric
While not a food per se, turmeric is certainly worth mentioning. Coming from the turmeric plant, turmeric is a spice bright in color and mostly known for its warm, bitter taste in curry dishes. In addition to its culinary use, turmeric has been used to treat an extensive number of inflammatory and infectious diseases and conditions, particularly related to its curcumin content. Curcumin, the chemical providing the vibrant color of turmeric, is suggested to reduce inflammation and combat against infection.